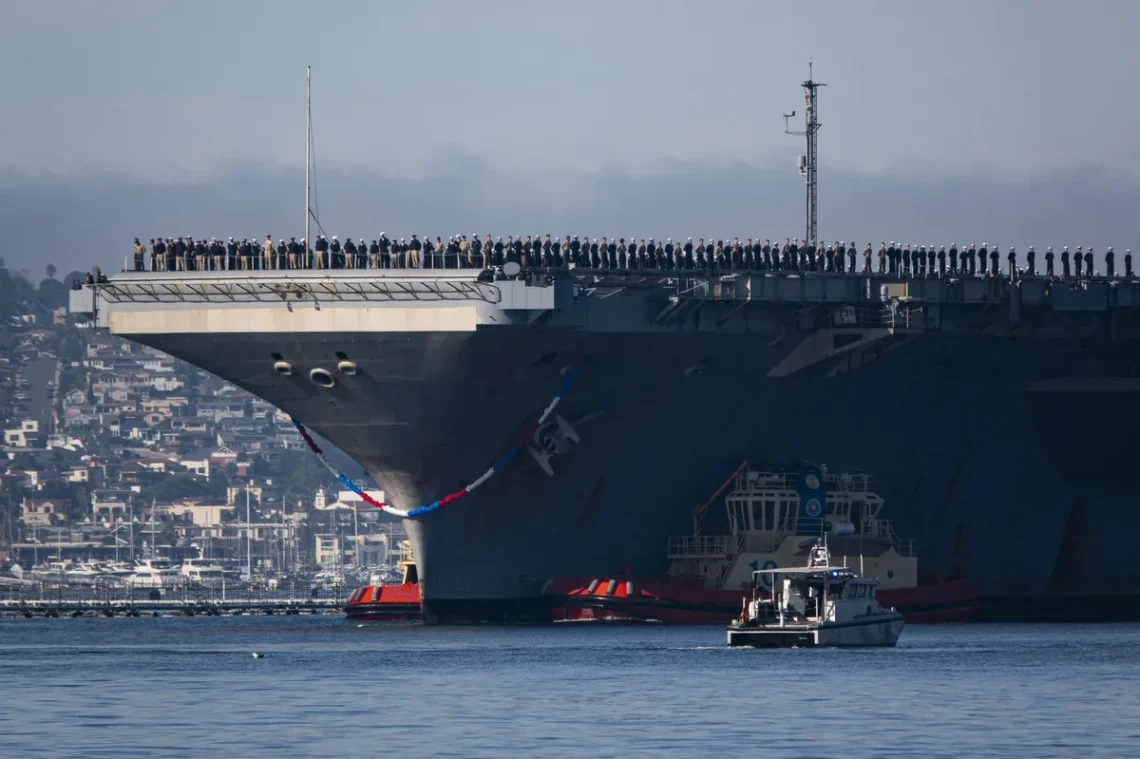
The announcement by the United States to construct a new generation of advanced battleships informally referred to as “Trump-class” has drawn significant international attention. While framed domestically as part of long-term naval modernization, the decision carries broader geopolitical meaning. At a time of rising global tensions and shifting power balances, the expansion of American naval capacity sends a clear strategic signal to allies and rivals alike.
For international observers, the move underscores a reality that has become increasingly apparent: maritime power remains central to global security and economic stability in the 21st century.
The Rationale Behind Naval Modernization
US defense officials argue that the naval expansion is a response to a rapidly evolving security environment. Increased military activity in the Indo-Pacific, renewed competition among major powers, and the need to protect global trade routes have all elevated the importance of naval strength.
Unlike land-based forces, navies enable sustained global presence. Aircraft carriers, destroyers, and advanced battleships allow the United States to project power, deter adversaries, and reassure allies across multiple regions simultaneously. In this context, the Trump-class initiative is presented as an investment in long-term strategic flexibility rather than a short-term political gesture.
Technology and the Future of Naval Warfare
Modern battleships are no longer defined solely by size or firepower. They integrate advanced radar systems, cyber-defense capabilities, missile interception technology, and unmanned platforms. US officials emphasize that the new class will be designed to operate in contested environments where cyber warfare, space-based surveillance, and precision weapons play decisive roles.
This technological emphasis reflects broader trends in military planning. Naval dominance today depends as much on information superiority and resilience as on traditional weaponry. From an international journalism perspective, this shift highlights how military competition increasingly overlaps with technological innovation.
Domestic Debate Over Cost and Priorities
The naval expansion has sparked debate within the United States. Supporters argue that maintaining maritime superiority is essential for national security and global stability. They contend that delayed investment would be more costly in the long run, particularly if strategic rivals close the technological gap.
Critics, however, question the financial burden. Large-scale naval projects require billions of dollars over decades, raising concerns about opportunity costs. Skeptics argue that resources could be directed toward domestic infrastructure, healthcare, or climate resilience.
This debate reflects a broader tension faced by many democracies: balancing external security commitments with internal economic and social priorities.
International Reactions and Strategic Signaling
Globally, reactions to the announcement have been mixed. US allies have largely welcomed the move, viewing it as reassurance of Washington’s commitment to collective security. For countries reliant on open sea lanes for trade, a strong US naval presence is often seen as a stabilizing force.
Rival powers, however, interpret the expansion differently. The construction of new battleships is viewed as escalation, reinforcing perceptions of an emerging arms competition. While no immediate confrontation is implied, the decision contributes to an atmosphere of strategic mistrust.
For international media, this divergence in interpretation underscores how military actions are often judged less by intent and more by perceived impact.
The Indo-Pacific Focus
Much of the strategic logic behind US naval modernization centers on the Indo-Pacific. The region has become the focal point of global economic activity and geopolitical rivalry. Ensuring freedom of navigation, deterring conflict, and maintaining alliance credibility are key objectives for Washington.
Naval power plays a crucial role in these goals. Unlike fixed bases, fleets can adapt quickly to changing conditions, offering both deterrence and crisis-response capabilities. The Trump-class ships are expected to enhance this flexibility, reinforcing the US role as a maritime power in the region.
A Broader Trend Toward Militarization
The US decision reflects a wider global trend. Many countries are increasing defense spending and modernizing armed forces in response to perceived threats. Naval expansion is particularly prominent, as control of sea lanes remains vital to economic security.
This trend raises concerns about an emerging arms race. While modernization can enhance deterrence, it also increases the risk of miscalculation. Without effective communication and confidence-building measures, military expansion may unintentionally heighten instability.
Economic and Industrial Implications
Beyond security, naval expansion has economic dimensions. Shipbuilding supports high-skilled jobs, technological development, and industrial capacity. For the United States, investing in naval infrastructure reinforces domestic defense industries and supply chains.
However, dependence on military production as an economic driver carries risks. Long-term sustainability depends on balancing defense needs with broader industrial and economic diversification.
Implications for Global Security
From a global perspective, the US naval expansion reinforces the central role of maritime power in international affairs. It highlights the persistence of traditional security concerns even as new challenges such as cyber threats and climate change gain prominence.
The decision also illustrates how security policies are increasingly shaped by perceptions of rivalry and uncertainty. In this environment, military signals carry heightened importance.
Conclusion: Power Projection in an Uncertain World
The construction of the Trump-class battleships marks more than a procurement decision; it represents a strategic statement about the United States’ role in the world. As competition among major powers intensifies, naval strength remains a key instrument of influence and deterrence.
For the international community, the challenge lies in managing this competition without tipping into confrontation. Whether naval modernization contributes to stability or fuels further rivalry will depend on diplomacy, transparency, and restraint as much as on firepower.